4 Ways That Describe Blockchain is the Future of Banking
You may have heard of Bitcoin, a new currency that was created in 2009. Bitcoin allows financial transactions, excluding middlemen – meaning, no banks! There were no transaction fees and no identity check. As time passes more merchants are beginning to accept Bitcoin.
The blockchain is the underlying technology that makes bitcoin work. There’s no central authority in a blockchain system. Rather, it is a peer-to-peer (P2P) network in which participating computers record transactions for inclusion in the public ledger they share. Any alterations made to public blockchains are publicly visible. This creates transparency and process integrity, as users can trust that transactions will be executed exactly as the protocol commands. Further, all transactions are immutable – meaning they cannot be altered or deleted.
These days, nearly every bank is experimenting with blockchain technology, as they try to unleash blockchain’s cost savings and operational efficiencies. According to a survey of 118 financial institutions, 55% believe that blockchain will fundamentally change banking, while 33% think that it is a determinant improvement. Only 11% regard it as a fad or just another technology innovation. [Euromoney, 2015]
An efficient tool for creating new financial services, infrastructure, and processes:
This technology will form the foundation of the next generation of financial services infrastructure. A recent survey by IBM found that 15% of top global banks intend to roll out full-scale, commercial blockchain products in 2017. [IBM, 2016]
In this survey of 200 banks, IBM concluded that 65% of banks expected to have blockchain projects in production within three years’ time. Larger banks (>100,000 employees) are leading the charge. The tech giant said that the major areas identified by lenders as ripe for blockchain-based innovation were: clearing and settlement, debt issuance and equity, wholesale payments, and reference data.
Simplified transactions compared to conventional payment systems:
Bitcoin is an example of how a decentralized automated financial system could utilize blockchain. While its current capabilities are still limited, it offers a compelling vision of the future, as blockchain technology acts as a self-regulating economic system.
For example, transactions must satisfy specific rules before getting accepted into the Bitcoin blockchain. Instead of writing rules and appointing a regulator to monitor for breaches, which is how the current financial system works, Bitcoin’s code sets the rules and the network checks for compliance. If a transaction breaks the rules (for example, if the digital signatures don’t match), it is rejected by the network.
Bitcoin’s “ monetary policy” is even written into its code: Issuance of new money every 10 minutes, with limited supply so there will only be 21 million Bitcoins ever. It’s a hard money rule similar to the gold standard (i.e., a system in which the money supply is fixed to a commodity and not determined by the government).
Blockchain reduces the cost of financial transactions:
In a traditional banking system, interbank transactions can take days for final settlement. With blockchain technology, transaction times can be reduced to mere and are processed 24/7. By stamping out the third-party mediator, blockchain technology represents exciting potential in its ability to simplify the transaction process.
Blockchain can streamline and transform trade finance:
The currently outdated processes that litter this area of banking, coupled with the sector’s overall size, means that it is ripe to be upgraded by distributed-ledger technology (blockchain). Furthermore, it appears to be among the top priorities for “ R3”, a global banking blockchain consortium, and one of the early leaders in blockchain development for the banking sector.
This New York-based company currently boasts a membership of over 80 banks and financial organizations. R3 managed to raise a record $107 billion in a fundraising round in May This was the largest single investment in blockchain to date, and the group is now close to launching its pilot commercial product. Eleven of the banks— HSBC, BBVA (Banco Bilbao Vizcaya Argentaria), BNP Paribas, ING, Intesa Sanpaolo, Mizuho, RBS (Royal Bank of Scotland), Bangkok Bank, Scotiabank, SEB, and US Bank—are preparing to use R3’s blockchain software “ Corda” to test an application aimed at cutting costs in the processing of “ sight letters of credit.” These will be payable immediately upon receipt of the letter and supporting documents by the relevant financial institution.
It’s the global banking system that could benefit the most from the implementation of blockchain’s revolutionary distributed-ledger technology. Whether considering payments, settlements, or compliance, blockchain’s key properties of decentralization, immutability, efficiency, cost-effectiveness and security have led to a growing chorus of support for the technology’s adoption across the entire spectrum of financial services. As such, the financial services industry is expected to undergo substantial disruption over the coming years.
Do you want to hire a software company that can develop blockchain technology for you? AppZoro Technologies is always here to help you!!
Also Read: [**Top 7 Tech Stack You Need to Look Out in 2022 & Ahead**](https://appzoro.com/blog/top-7-tech-stack-you-need-to-look-out)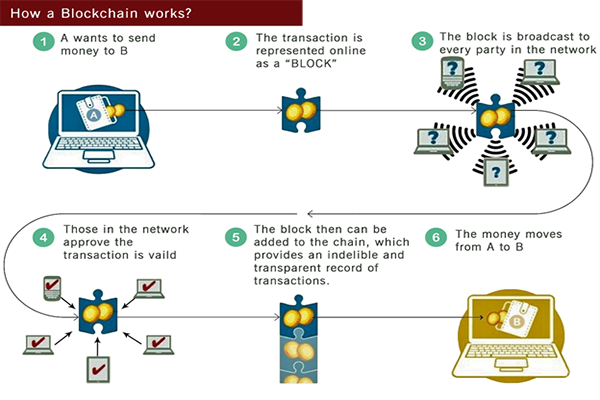
Leave a Comment